Porous Fibers Innovation Expert
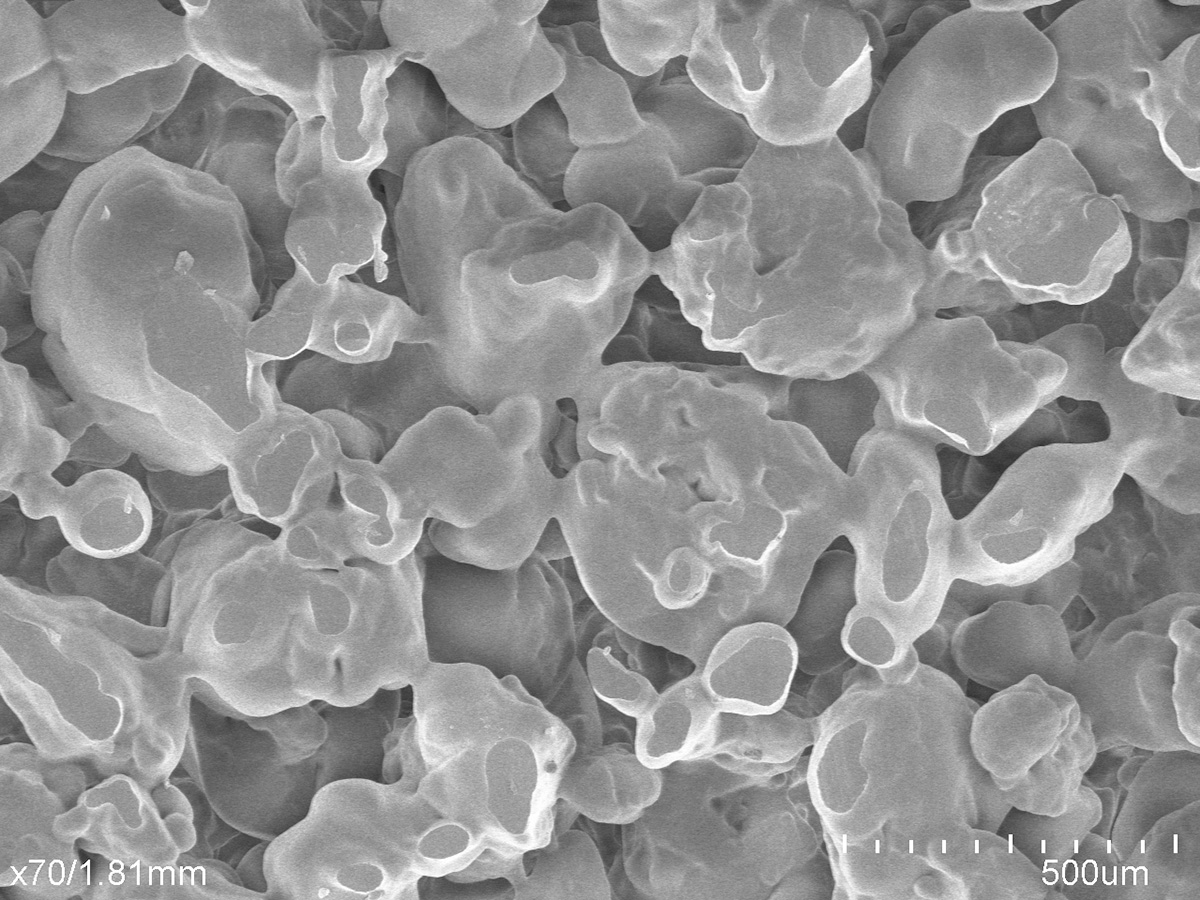
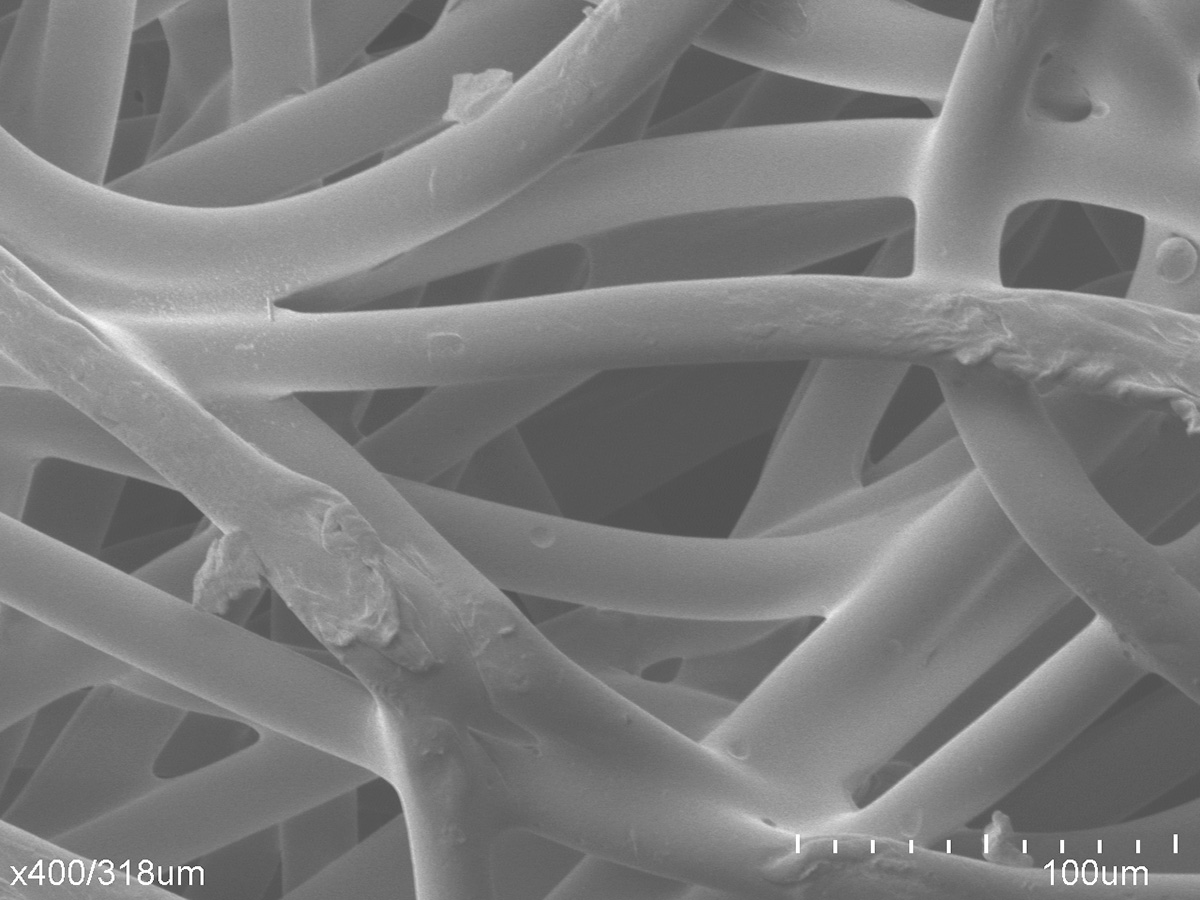
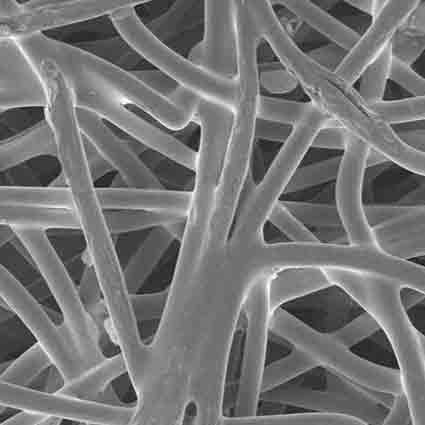
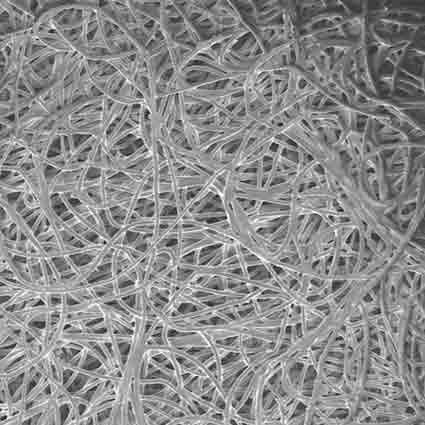
Porous fiber consists of bonded fibrous strands which create two-dimensional cross-sections that can be extruded to create three-dimensional shapes. Between the directionally aligned fibrous strands are voids, or pores, which can be independently controlled for fluid management applications that require faster flow or greater absorption of liquids.
These bicomponent fiber materials have an inner core and outer sheath that provide an ideal capillary structure for liquid transfer, filtration, and diffusion applications where wicking speed, wicking distance, filtration efficiency, and flow resistance are key drivers of the device’s performance.
Made from a variety of thermoplastic materials with varying properties, our materials are moldable for high-volume applications and customizable for easy fabrication and conversions. We provide large sheets, rolls, or other material formats specific to your needs.


Talk with a Material Science Expert
Manufacturing process
Porous fiber uses heat and pressure in the bonding process similar to sintered porous plastics. Instead of bonding particles, though, it bonds fibrous strands. A sheath is wrapped around customized fibers and the fibers are bonded in various configurations. This does not involve knitting or weaving, but rather forming fibrous components such as sheets, rods, tubes, blocks, and 3D geometrics.
Watch the process
Options for customizing porous fiber

Register for Our On-Demand Webinar
Intro to Porous Fiber
Common applications for porous fiber
Wick
Wicking works extremely well with porous fiber, as capillary forces are able to promote ease of fluid transfer in applications such as point-of-care diagnostic sample testing, dialysis treatments, and commercial applications such as inkjet printing cartridges.
Filter
Porous fibers can help to separate a solid or liquid from a mixture. Some of these applications include automotive oil & fuel water separation filters, injectable and applicator glass shard filters for life science applications, as well as liquid contaminant removal filters for consumer and industrial segments.

Diffuse
Porous fiber solutions can offer precision control over the diffusion rate in applications such as bioprocessing spargers, plug-in air fresheners, as well as insecticides.

Apply
Application products such as whiteboard marketers work great with porous fiber nibs. The material allows the ink to apply evenly and completely onto a surface or substrate.
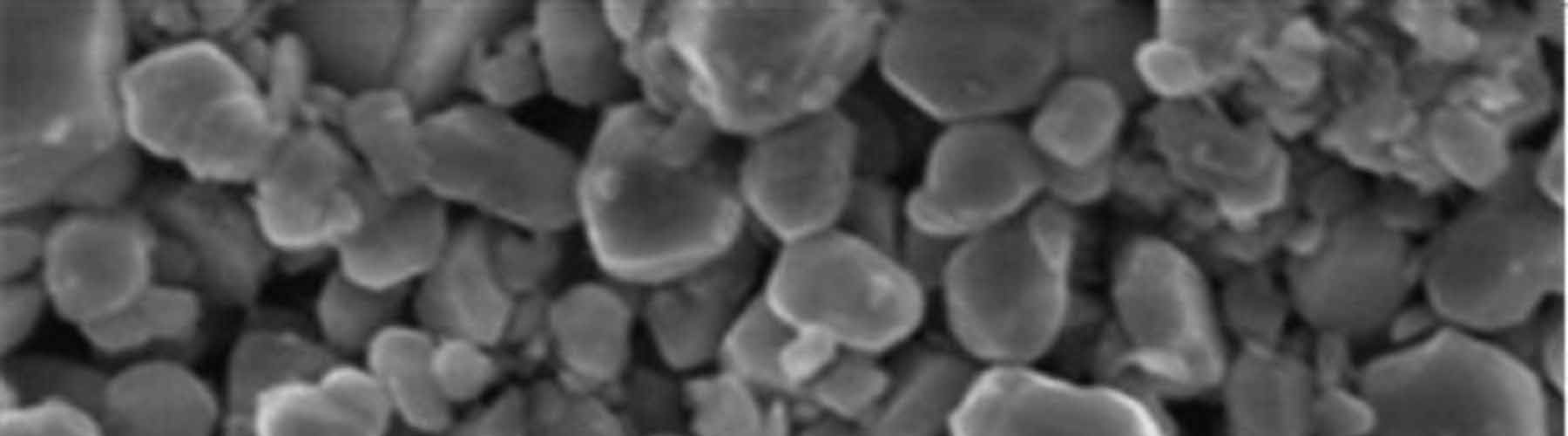
Why do pore size and flow matter?
Learn more in our new technical article
Related Resources

Porex: The Perfect Fit Brochure
Experience Porex’s customizable porous media capabilities. From advanced filtration media to cutting-edge fluid management, our unmatched material science expertise and extensive global manufacturing network help you unlock new frontiers of innovation and efficiency.

Understanding the Fiber Bonding Process
The video demonstrates how Porex utilizes synthetic fiber binding processes to produce components.

What Is Porous Plastic?
Read how porous plastic is formed as a component to control the flow of gases, liquids, light, or sound.

Understanding Pore Size Distribution
In this video, learn how to measure the space between the particles and it’s effect on component performance.



