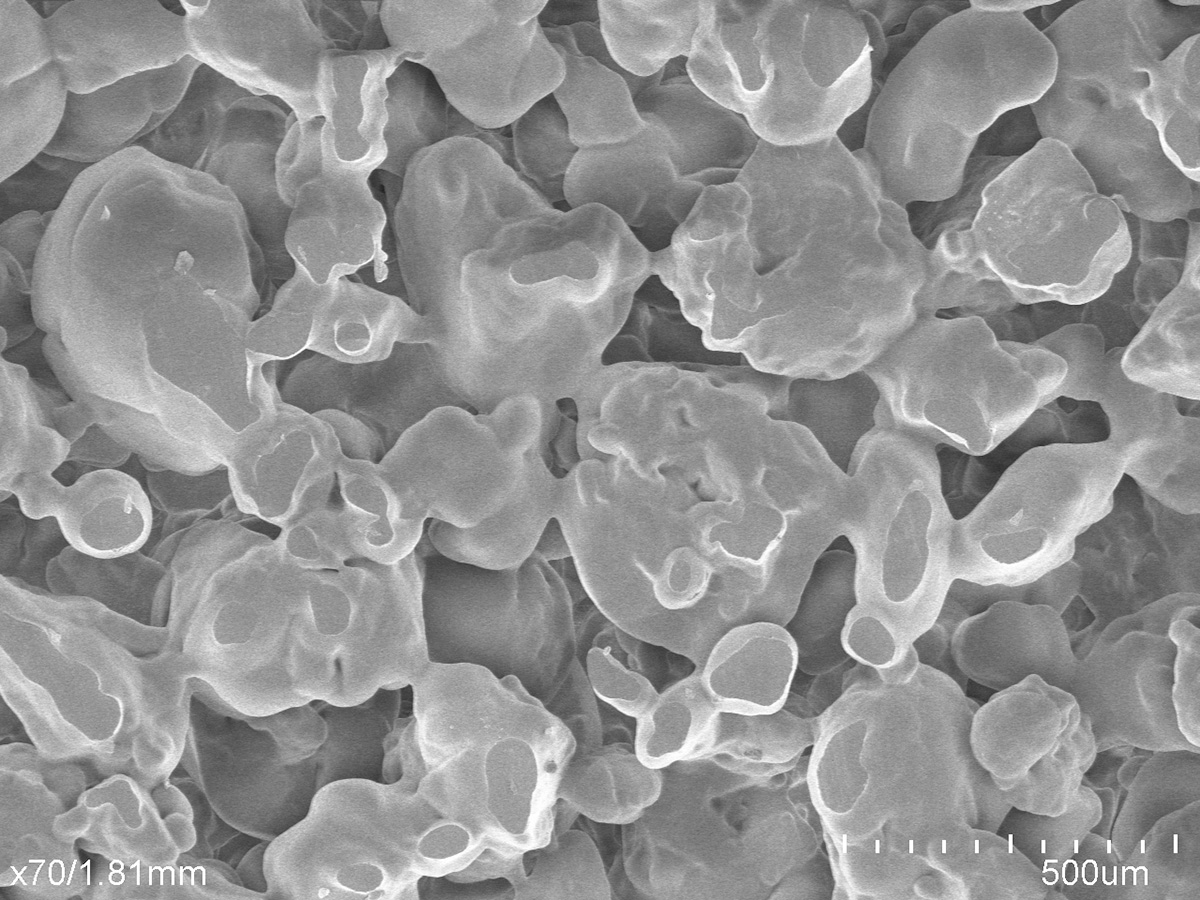
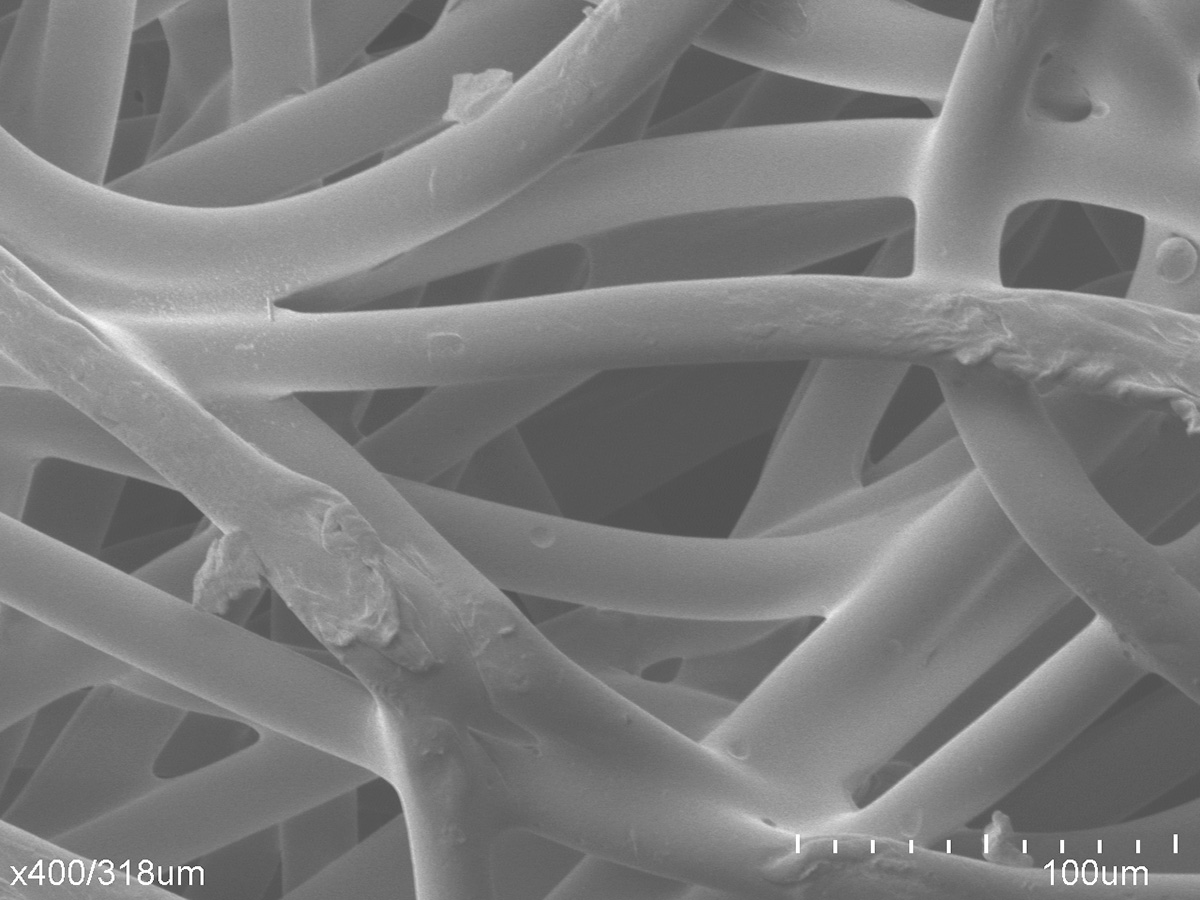
What is the function of Absorption?
Absorption is one of the most common – and crucial – means of controlling liquids and contaminants. It is the physical and/or chemical process during which atoms or molecules of one material enter the bulk of another. In cleaning applications, a material’s capacity to absorb and trap contaminants can mean the difference between a sterile or compromised environment. In medical applications, a material’s capacity to absorb and contain liquids like blood and exudations can mean the difference between life and death. Porex uses a variety of polymeric-bonded fiber and polyurethane foam technologies to achieve a regulated absorption.
Porex provides wound care dressing manufacturers with advanced material solutions that have increased absorptive capacity, greater tear strength, and high fluid retention under compression – without compromising softness and comfort. Our medical-grade foam-fiber hybrid material features a fiber web throughout a super-soft hydrophilic foam matrix. This dramatically increases absorbency while enhancing overall performance and comfort in critical medical applications requiring treatment of acute and chronic wounds. Other applications that our absorption materials can support include biological sample testing, gas absorption sensors, carbon odor eliminators, and makeup applicators among others.

Talk with a Material Science Expert
Webinar
In this webinar preview, explore absorption media solutions as we discuss:
- What drives physical absorption
- How chemical absorption works
- The typical problems that are solved by absorbents
You’ll get all the details about why absorption is critical in certain industry applications, the types of porous polymers that are required for successful absorption, and so much more.
How absorption works in porous polymers
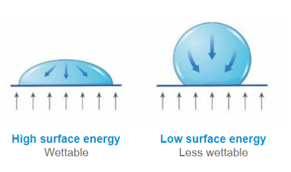
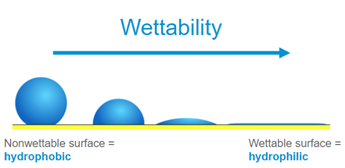
Absorption is a bulk phenomenon which can be achieved physically, chemically or both. The material being absorbed is called an absorbate, and the absorption material is called an absorbent. Absorption works as an absorbent takes in a liquid or gas through means of capillary action – the force through which fluid can travel in tight spaces without or against external forces like gravity. A material’s pore size, or void space, and surface energy relative to the liquid absorbate can have a direct effect on capillary action along with important functions such as fluid flow rates, contaminant holding capacity, and absorption speed, among others. A high surface energy means there is a strong molecular attraction present, therefore, it is easier for the liquid to bond to the solid material, whereas a low surface energy signals a weak molecular attraction, making it harder to bond. For absorption to take place, a high surface energy needs to be present to create a wettable surface.
Why do pore size and flow matter?
Learn more in our new technical article
Design challenges that absorption media can solve
- Collecting and holding a biological sample for testing, such as a saliva test
- Holding an electrolyte solution that will absorb or react with unwanted gases in a sensor device
- Collecting and holding unwanted house odors such as carbon odor eliminators
- Absorbing noise produced by pneumatic tools for a more pleasant work environment
- Absorbing fluid exudate in wounds to help patients heal faster
- Absorbing a makeup formula on an applicator for transfer to the skin

Related Technologies
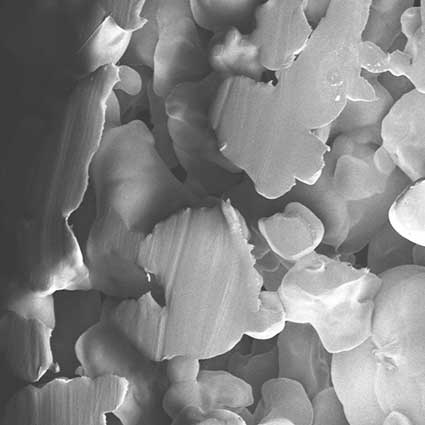

Sintered Porous Plastics
Sintered porous plastics are created using a combination of heat and pressure to bond the materials together.
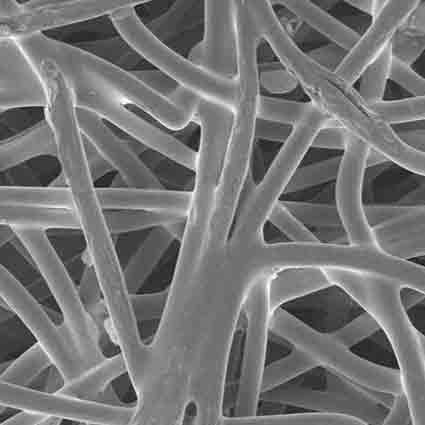

Porous Fiber
Porous fibers consist of bonded fibrous strands which create two-dimensional cross-sections that can be extruded to create three-dimensional shapes.
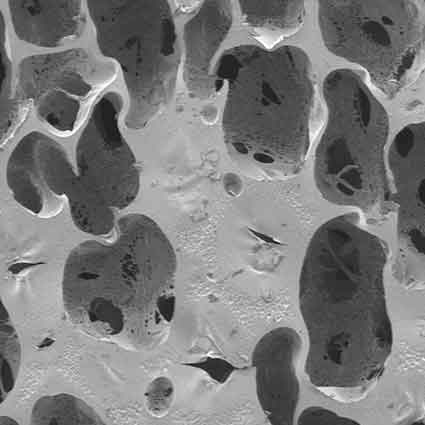
Porous Foam
Our porous foam consists of wide-ranging densities, porosities, and levels of softness for both medical and cosmetic applications.

Register for our On-Demand Webinar
Mastering Absorption: Controlling Liquid Retention & Release with Porous Polymers




